Table of Contents
- Introduction to Impella: A Breakthrough in Cardiac Support
- How the Impella Heart Pump Works
- Types of Impella Devices & Their Applications
- Impella vs ECMO: A Comparative Analysis
- Clinical Indications: When Is Impella Used?
- Insertion Procedure: How Is Impella Deployed?
- Advantages of Impella in Cardiogenic Shock Management
- Risks, Complications & Patient Selection Criteria
- Latest Innovations & Future of Impella Technology
- FAQs: Everything You Need to Know About Impella
1. Introduction to Impella: A Breakthrough in Cardiac Support
The Impella heart pump is a game-changing percutaneous mechanical circulatory support (pMCS) device designed to provide temporary cardiac assistance in critically ill patients. With its minimally invasive design and efficient hemodynamic support, Impella is widely used in cases of cardiogenic shock, high-risk PCI, and acute heart failure.
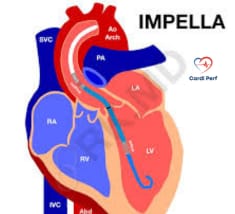
2. How the Impella Heart Pump Works
The Impella device is a catheter-based micro-axial flow pump that is percutaneously inserted through the femoral artery or axillary artery. It works by:
- Unloading the left ventricle, reducing myocardial oxygen demand.
- Enhancing cardiac output up to 5.5 L/min.
- Maintaining end-organ perfusion, preventing multi-organ failure.
💡 Impella serves as a bridge-to-recovery or bridge-to-decision for critically ill patients.
3. Types of Impella Devices & Their Applications
H3: Impella CP (Cardiac Power)
- Flow rate: ~3.5 L/min
- Used for high-risk PCI and cardiogenic shock.
H3: Impella 5.0 & Impella 5.5
- Flow rate: Up to 5.5 L/min
- Ideal for post-cardiotomy cardiogenic shock & LV support.
H3: Impella RP (Right Ventricular Support)
- Used for right heart failure and RV infarction.
H3: Impella ECP (Expandable Cardiac Power)
- Newest innovation designed for even less invasive LV support.
4. Impella vs ECMO: A Comparative Analysis
| Feature | Impella | ECMO |
|---|---|---|
| Cardiac Support | Primarily LV support | Full cardiopulmonary support |
| Insertion | Percutaneous via femoral/axillary artery | Cannulation via large vessels |
| Oxygenation | No oxygenation support | Provides full oxygenation |
| Flow Rate | Up to 5.5 L/min | 3–7 L/min |
| Best Used For | LV unloading, Cardiogenic shock, PCI | Cardiac arrest, respiratory failure |
🚀 Impella offers superior LV unloading, while ECMO is better for complete cardiac-respiratory support.
5. Clinical Indications: When Is Impella Used?
Impella is primarily indicated for:
✅ Cardiogenic Shock (AMI, Post-Cardiotomy, Myocarditis)
✅ High-Risk PCI (Unprotected Left Main, Severe CAD, LV Dysfunction)
✅ Bridge to Recovery or Bridge to Decision
🩺 Early Impella deployment significantly improves patient survival!
6. Insertion Procedure: How Is Impella Deployed?
Step-by-Step Guide:
1️⃣ Femoral or axillary artery access using percutaneous technique.
2️⃣ Advancement into the left ventricle under fluoroscopic guidance.
3️⃣ Pump activation, enabling LV unloading.
4️⃣ Monitoring & Weaning as per hemodynamic response.
💡 The Impella procedure takes less than 15 minutes!
7. Advantages of Impella in Cardiogenic Shock Management
🔹 Rapid LV unloading → Reduces ischemic injury
🔹 Increased cardiac output → Improves end-organ perfusion
🔹 Minimally invasive → Faster recovery & reduced complications
📢 Impella is the preferred choice for hemodynamic stabilization in acute heart failure!
8. Risks, Complications & Patient Selection Criteria
H3: Risks & Complications
⚠️ Vascular complications (bleeding, hematoma, limb ischemia)
⚠️ Hemolysis due to high-speed rotor
⚠️ Device migration affecting efficacy
H3: Ideal Patient Selection Criteria
✔️ EF < 35% with hemodynamic instability
✔️ Cardiogenic shock (post-AMI, post-cardiotomy)
✔️ High-risk PCI requiring temporary LV support
👨⚕️ Proper patient selection and skilled implantation are key to successful outcomes!
9. Latest Innovations & Future of Impella Technology
🔬 Impella 5.5 SmartAssist: Real-time hemodynamic monitoring
🔬 New AI-driven algorithms: Predicting patient deterioration early
🔬 Percutaneous Biventricular Support (BIVAD): Next-gen therapy in cardiogenic shock
🚀 The future of Impella technology is pushing boundaries in mechanical circulatory support!
10. FAQs: Everything You Need to Know About Impella
Q1: How long can an Impella device stay in place?
A: Impella can be used for up to 7 days, depending on the patient’s condition.
Q2: Can Impella be used in combination with ECMO?
A: Yes! ECpella (ECMO + Impella) strategy is often used to unload the LV while maintaining oxygenation.
Q3: How does Impella compare to an intra-aortic balloon pump (IABP)?
A: Impella provides superior hemodynamic support (5.5 L/min vs. 0.5 L/min) and is more effective in cardiogenic shock.
Q4: Is Impella suitable for all cardiogenic shock patients?
A: No. Contraindications include severe aortic regurgitation, LV thrombus, and severe PAD.
visit us on cardiperf.com for latest updates about cardiac perfusion science, 🚀🔥