Perfusion science has seen remarkable evolution in recent years, with the advent of new technologies and approaches that aim to enhance patient outcomes during cardiac surgery and other critical procedures. If you’re a perfusionist or healthcare professional working in the cardiac field, staying ahead of these current practices and emerging trends is crucial for improving patient care and optimizing your practice. Here’s a breakdown of what’s currently shaping the field of cardiac perfusion, and where it’s heading in the future.
Current Practices in Perfusion Science
1. Cardiopulmonary Bypass (CPB) Optimization
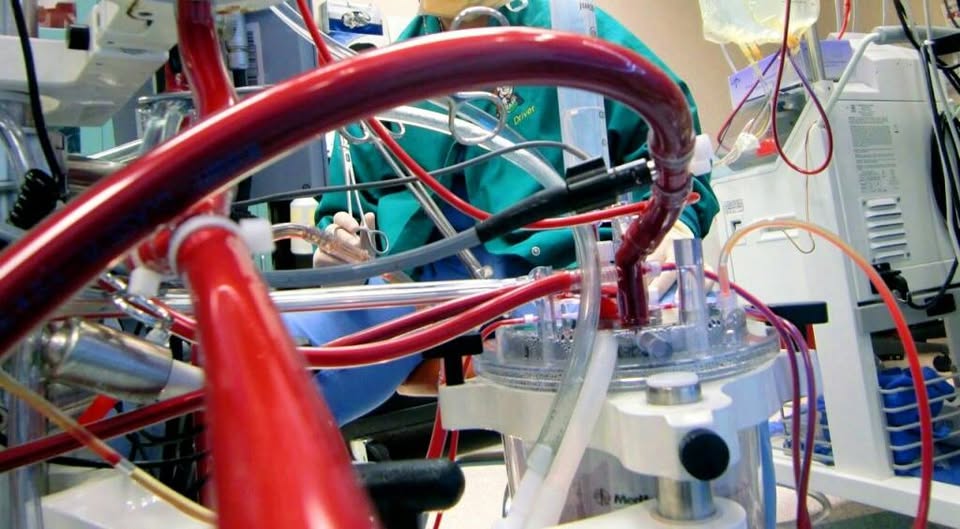
Cardiopulmonary bypass (CPB) is a core component of many cardiac surgeries, including coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG) and heart valve repair/replacement. Modern practices focus on optimizing oxygen delivery and perfusion to minimize complications. Perfusionists are now using miniaturized CPB systems that reduce priming volume, minimize hemodilution, and improve outcomes by providing more precise control over blood flow.
2. ECMO (Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation)
Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO) has become a life-saving tool in critical cardiac and respiratory failure cases. Whether as a bridge to recovery or heart transplantation, ECMO is being used with increasing frequency. Pediatric ECMO, in particular, is advancing, with specialized circuits designed to cater to younger patients. Understanding how ECMO integrates with perfusion science is a vital area for those involved in pediatric congenital heart disease management.
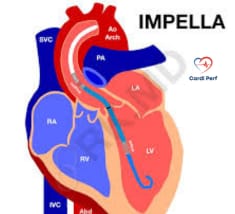
3. Intra-Aortic Balloon Pump (IABP)
Intra-aortic balloon pumps are essential in supporting patients with severe heart failure or shock. The current trend in IABP therapy is combining it with other circulatory support devices, such as Impella or Ventricular Assist Devices (VADs), to maximize cardiac output and improve perfusion in high-risk patients.
4. Autologous Blood Recovery with Cell Saver
Cell saver technology, which recovers blood lost during surgery for autotransfusion, is a growing practice, especially in cardiac surgeries. Using autologous blood can reduce the need for donor blood transfusions, minimizing the risk of complications such as transfusion reactions and infections. This practice is becoming a standard in minimally invasive cardiac surgery.
5. Anticoagulation Monitoring
Precise anticoagulation management is critical during cardiac surgery. Techniques like ACT (Activated Clotting Time) and TEG (Thromboelastography) are used to monitor and tailor anticoagulation therapy to each patient’s unique needs, minimizing the risk of bleeding or clot formation during surgery.
Emerging Trends in Perfusion Science
1. Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning
AI and machine learning are paving the way for predictive analytics in perfusion science. AI tools are now being integrated into cardiac surgery protocols to anticipate complications like hypotension, clotting, or perfusion failure in real-time. This helps perfusionists take preemptive action, reducing risks and enhancing patient care.
2. 3D Printing and Personalized Perfusion Circuits
3D printing technology is revolutionizing the way perfusionists design and build equipment. Customized perfusion circuits tailored to each patient’s unique anatomy improve the efficiency of the perfusion process, reduce blood trauma, and increase the precision of surgical procedures. The future of personalized cardiac surgery lies in creating specific, patient-centric solutions using cutting-edge 3D technology.
3. Biocompatible Materials
Research is focusing on biocompatible materials that reduce the inflammatory response triggered by foreign substances in the body during perfusion. These materials improve the patient recovery rate, decrease post-surgery complications, and enhance the overall effectiveness of extracorporeal circuits such as ECMO and CPB systems.
4. Total Artificial Heart (TAH) and Long-Term Mechanical Circulatory Support
Long-term circulatory support with devices like the Total Artificial Heart (TAH) is on the rise. This technology is offering life-saving solutions for patients who are ineligible for heart transplants. Perfusionists play a pivotal role in managing these devices, optimizing oxygenation, and ensuring long-term perfusion support for critically ill patients.
5. Hemofiltration and CRRT in ECMO Patients
Integrating Continuous Renal Replacement Therapy (CRRT) with ECMO is an emerging trend to improve fluid and electrolyte balance in patients with kidney failure. This combined approach is helping optimize renal function in patients undergoing complex surgeries or facing acute kidney injury.
6. Remote ECMO Management via Telemedicine
Telemedicine is gaining traction, allowing healthcare professionals to remotely monitor and manage ECMO patients. Remote perfusion monitoring enables perfusionists to assess circuit functionality, oxygenation levels, and other vital parameters from a distance, improving the efficiency and accessibility of care.
7. Non-Invasive Monitoring Technologies
The rise of wearable sensors and non-invasive monitoring devices allows for continuous tracking of a patient’s hemodynamic status. These devices track metrics like oxygen saturation, blood pressure, and heart rate, making patient management less invasive and more efficient, especially for post-operative care.
What’s Next for Perfusion Science?
Looking ahead, personalized perfusion will be at the forefront of cardiac care. Expect greater integration of genetic profiles and real-time data to create highly individualized perfusion strategies. Advancements in bioprinting, AI, and robot-assisted perfusion are set to redefine patient care in cardiac surgery, allowing for faster, more accurate interventions.
Frequently asked questions FAQs about it
1. What is perfusion science, and why is it important in cardiac surgery?
Answer: Perfusion science focuses on the management of blood flow during surgery, especially when the heart and lungs need to be temporarily bypassed. It’s critical in cardiac surgery as it ensures the body receives adequate oxygenation and nutrient delivery while the heart undergoes repair or other procedures. Perfusionists manage machines like CPB and ECMO to maintain these vital functions.
2. How does ECMO work, and when is it used in cardiac care?
Answer: ECMO (Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation) is a life-support system that temporarily takes over the function of the heart and lungs. It’s used for patients experiencing severe cardiac or respiratory failure. ECMO circulates blood through an external oxygenator and pump, allowing the heart and lungs to rest and recover. It’s commonly used in patients awaiting heart transplant or during severe complications like cardiac arrest.
3. What are the advantages of using cell saver technology in cardiac surgery?
Answer: Cell saver technology allows for the recovery of a patient’s own blood lost during surgery. This is then filtered and returned to the body. The advantages include reducing the need for donor blood transfusions, minimizing risks of transfusion reactions, and lowering the chances of infection or immune response, making recovery safer and faster.
4. How does IABP (Intra-Aortic Balloon Pump) support heart function during surgery?
Answer: The IABP is a mechanical device that assists the heart by inflating and deflating a balloon inside the aorta during the cardiac cycle. This reduces the workload on the heart and improves blood flow to vital organs. It is commonly used in high-risk surgeries, such as CABG (coronary artery bypass grafting), and in cases of heart failure or shock.
5. What role does AI play in modern perfusion science?
Answer: AI and machine learning are transforming perfusion science by enabling predictive analytics. These tools can anticipate complications such as clot formation, hypotension, or hemodynamic instability in real-time. AI systems analyze vast amounts of data from patient monitoring systems, allowing perfusionists to make more informed, proactive decisions and improve patient outcomes.
6. How are biocompatible materials changing perfusion technology?
Answer: The development of biocompatible materials helps reduce the inflammatory response triggered during perfusion, especially during cardiopulmonary bypass (CPB) and ECMO. These materials are designed to better integrate with the human body, reducing complications such as clotting or organ dysfunction, and improving patient recovery after surgery.
7. What is CRRT (Continuous Renal Replacement Therapy), and why is it used in perfusion science?
Answer: CRRT is a form of dialysis used to manage patients with acute kidney injury, especially in critically ill individuals. In perfusion science, CRRT is often combined with ECMO to help balance fluid, electrolytes, and toxins in patients who are on mechanical circulatory support. This combination helps optimize renal function and enhances overall recovery.
8. How do personalized perfusion circuits improve patient outcomes?
Answer: Personalized perfusion circuits are custom-designed to match a patient’s specific anatomy and physiological needs. These circuits help improve the precision of oxygen delivery, reduce blood trauma, and increase the efficiency of the perfusion process. With 3D printing and other advancements, perfusionists can create circuits that are tailored to each individual, enhancing surgical outcomes.
9. What are the latest advancements in pediatric ECMO for congenital heart disease?
Answer: In pediatric patients, particularly those with congenital heart disease, advancements in ECMO include more age-appropriate circuits and improved monitoring technologies. These innovations allow perfusionists to better support neonatal and pediatric patients, reducing the risks associated with ECMO and improving long-term recovery. Pediatric ECMO has become more successful, with greater survival rates for critically ill infants and children.
10. What is the future of perfusion science?
Answer: The future of perfusion science will likely be shaped by personalized medicine, where genetic and molecular profiling help tailor perfusion techniques to each patient’s unique needs. Innovations such as AI integration, bioprinting, and robot-assisted perfusion are set to redefine cardiac care, providing more efficient, effective, and less invasive treatments for patients undergoing complex cardiac surgeries.
Stay Updated with Cutting-Edge Perfusion Insights
For in-depth articles on cardiac surgery, ECMO management, and innovations in perfusion science, don’t forget to visit CardiPerf.com. Our blog features expert insights and best practices for perfusionists, cardiac surgeons, and healthcare professionals.