Echocardiography has become indispensable in the diagnosis and management of heart conditions. This non-invasive imaging technique offers real-time visualization of the heart’s structure and function, empowering healthcare professionals to make informed decisions – especially in critical situations. This guide explores the world of echocardiography, from its basic principles to its diverse uses in modern medicine.
Table of Contents
2. What is an Cardiac ultrasound?
An echocardiogram uses ultrasound waves to create images of the heart. A transducer, placed on the chest or passed down the esophagus, emits sound waves that bounce off the heart’s structures. These echoes are processed by a computer to generate moving images, revealing the chambers, valves, and blood flow.
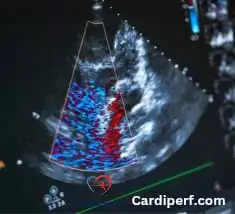
3. Types of Heart imaging : A Closer Look
Several types of echocardiograms exist, each designed for specific diagnostic needs:
3.1 Transthoracic Echocardiography (TTE): The Standard View
TTE is the most common type. The transducer rests on the chest, transmitting ultrasound waves through the chest wall. Angles for assessment in TTE include parasternal long and short axis views, apical four-chamber, and subcostal views, each providing unique perspectives on cardiac structures and function.
3.2 Transesophageal Echocardiography (TOE): When Clarity Matters
TOE involves passing a transducer down the esophagus, providing clearer images, especially when structures are obscured by the chest wall. TOE offers superior visualization of posterior structures like the left atrium and mitral valve, crucial for diagnosing conditions like aortic dissection.
3.3 Stress Echocardiography: Assessing Heart Function Under Stress
Stress echocardiography is performed during exercise or with medication to assess how the heart responds to stress, helping detect coronary artery disease.
3.4 Contrast Echocardiography: Enhancing the Image
Contrast agents are injected into the bloodstream to enhance images and improve visualization of specific cardiac structures, useful for evaluating intracardiac shunts.
3.5 Surgical Echocardiography: Real-Time Insights in the OR
Surgical echo provides real-time assessment during cardiac surgery, allowing surgeons to evaluate repairs and optimize outcomes.
4. Echo in Emergency Situations: Critical Applications
Echocardiography is vital in the rapid assessment and management of cardiac emergencies:
- Chest Pain Diagnosis: An emergency echocardiogram can quickly differentiate cardiac from non-cardiac causes of chest pain.
- Suspected Acute Myocardial Infarction: A STAT echo is crucial for rapid diagnosis and treatment of heart attacks.
- The Emergency Department: Urgent echo is essential for evaluating unstable patients.
- Unstable Patients: Echo protocols guide assessment and management in critical situations.
- Trauma Assessment: Point-of-care echo allows rapid assessment of cardiac function in trauma patients.
- Emergency Situations: Focused cardiac ultrasound (FOCUS) helps quickly assess cardiovascular wellness
- Pulmonary Embolism: Echocardiography in the ED can aid in diagnosing pulmonary embolism.
- Dyspnea: Emergency echo helps differentiate cardiac from non-cardiac causes of shortness of breath.
- Cardiac Tamponade: Echo is essential for diagnosing and managing cardiac tamponade.
- Cardiac Arrest: Echo can assist in guiding management during cardiac arrest.
- Critically Ill Patients: Portable echo allows rapid assessment of heart function.
- Acute Decompensation: Echo helps evaluate valvular heart disease in acute decompensation.
- Shock: Emergency echo assists in assessing fluid status in shock.
- Pericardiocentesis: Echo guides pericardiocentesis in emergency settings.
- Emergency Echo Interpretation: How to interpret an emergency echocardiogram quickly and accurately is a crucial skill.
- Acute Aortic Dissection: Echocardiography TOE plays a vital role in diagnosing acute aortic dissection.
- Intraoperative Assessment: Surgical echo is indispensable for mitral valve repair and other cardiac surgeries.
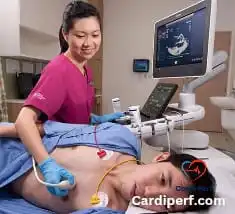
5. Echo’s Role in Cardiac Conditions
Echo is crucial in diagnosing and monitoring various conditions, including heart failure, valvular heart disease, congenital heart defects, cardiomyopathy, pericardial effusion, pulmonary hypertension, and infective endocarditis.
6. Benefits and Limitations of Echo
- Benefits: Non-invasive, real-time visualization, portable, cost-effective.
- Limitations: Image quality can be affected by body habitus, operator dependence, limited visualization of certain structures.
7. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- What is the difference between TTE and TOE? TTE is performed on the chest, while TOE involves passing a transducer down the esophagus, providing clearer images.
- Is echocardiography painful? Echocardiography is generally painless. You may feel some pressure from the transducer on your chest.
- How long does an echocardiogram take? A standard echocardiogram typically takes 30-60 minutes.
- Are there any risks associated with echocardiography? Echocardiography is a very safe procedure with minimal risks.
- Can echo detect all heart problems? While echo is a powerful tool, it may not detect all heart conditions. Other tests may be necessary.
- How often should I get an echocardiogram? The frequency of echocardiograms depends on your individual health condition and risk factors. Your doctor will determine the appropriate schedule.
- What is the role of echo in heart failure management? Echo helps diagnose heart failure, assess its severity, and guide treatment decisions.
- Can echo be used to diagnose congenital heart defects? Yes, echo is a crucial tool in diagnosing congenital heart defects in both children and adults.
- How is stress echocardiography performed? Stress echocardiography is performed during exercise or with medication to assess how the heart responds to stress.
- What is the significance of How to Interpret an Emergency Echocardiogram Quickly and Accurately? Rapid and accurate interpretation of emergency echocardiograms is crucial for timely diagnosis and treatment of life-threatening cardiac conditions
8. Conclusion: The Future of Cardiac Imaging
Echo has become an indispensable tool in modern cardiology. Its non-invasive nature, portability, and versatility make it invaluable. As technology advances, echocardiography will continue to play a crucial role in improving patient outcomes. For updates regarding cardiovascular Perfusion Science visit us at cardiperf.com