Table of Contents:
- Introduction: Unveiling the Power of Myocardial Perfusion Imaging
- What is Myocardial Perfusion Imaging? 2.1 How Does Cardiac Perfusion Imaging Work? 2.2 Types of Myocardial Perfusion Imaging 2.2.1 Exercise Stress MPI 2.2.2 Pharmacological Stress MPI
- Benefits of MPI
- Myocardial Perfusion Imaging vs. Other Cardiac Tests 4.1 MPI vs. Stress Test 4.2 MPI vs. Cardiac CT Angiography 4.3 MPI vs. Echocardiogram
- Preparing for a Myocardial Perfusion Imaging Study
- The Heart Health Assessment Procedure: What to Expect
- Understanding Your Myocardial Perfusion Imaging Report
- Clinical Applications of Myocardial Perfusion Imaging 8.1 Diagnosing Coronary Artery Disease (CAD) 8.2 Assessing Heart Attack Risk 8.3 Evaluating Chest Pain (Angina) 8.4 Guiding Treatment Decisions
- Coronary Blood Flow in Special Populations 9.1 Patients with Pacemakers 9.2 Patients with Diabetes
- Advancements in Heart Scan
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- Conclusion: Empowering Cardiac Care with Myocardial Perfusion Imaging
1. Introduction: Unveiling the Power of Myocardial Perfusion Imaging
Cardiovascular disease remains a leading cause of morbidity and mortality worldwide. Early and accurate diagnosis is paramount for effective management. Myocardial Perfusion Imaging (MPI), also known as a Myocardial Perfusion Scan or simply a Heart Scan, is a non-invasive diagnostic technique that plays a crucial role in assessing cardiac health. This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of MPI, exploring its benefits, procedures, applications, and its significance in contemporary cardiac care.
2. What is Myocardial Perfusion Imaging?
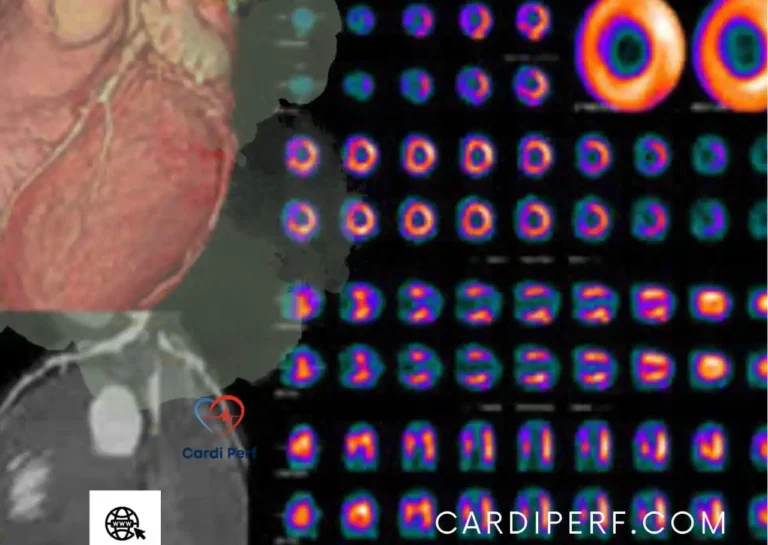
Myocardial Perfusion Imaging is a nuclear imaging technique used to visualize blood flow to the heart muscle (myocardium). It utilizes a radioactive tracer, injected into the bloodstream, which is absorbed by the heart muscle in proportion to blood flow. A special camera then detects the radiation emitted, creating images that reveal areas of adequate or reduced perfusion.
2.1 How Does Cardiac Perfusion Imaging Work?
The principle behind MPI is that healthy heart muscle receives adequate blood flow, while areas with narrowed or blocked arteries (due to conditions like Coronary Artery Disease (CAD)) receive less. The radioactive tracer concentrates in areas with good blood flow, creating brighter spots on the images. Areas with reduced blood flow appear darker or fainter, indicating potential ischemia (lack of oxygen).
2.2 Types of Myocardial Perfusion Imaging
MPI is typically performed in conjunction with a stress test to increase the heart’s workload and reveal any flow limitations that might not be apparent at rest.
2.2.1 Exercise Stress MPI
In this type, the patient exercises on a treadmill or stationary bike while the tracer is injected. This increases the heart rate and demand for blood flow.
2.2.2 Pharmacological Stress MPI
For patients who cannot exercise, a medication (like adenosine or dobutamine) is used to simulate the effects of exercise on the heart.
3. Benefits of MPI
- Non-invasive: No surgical procedures are required.
- Accurate: Highly effective in detecting CAD and ischemia.
- Risk stratification: Helps assess the risk of future cardiac events.
- Treatment planning: Guides decisions about medical therapy, angioplasty, or bypass surgery.
- Prognosis: Provides valuable information about the long-term outlook for patients with heart disease.
4. Myocardial Perfusion Imaging vs. Other Cardiac Tests
4.1 MPI vs. Stress Test
While often used together, the traditional stress test (ECG) primarily assesses electrical activity of the heart. MPI provides direct visualization of blood flow, offering more detailed information about myocardial perfusion.
4.2 MPI vs. Cardiac CT Angiography
Cardiac CT angiography uses X-rays and contrast dye to visualize coronary arteries. While it can detect blockages, MPI provides functional information about blood flow, which is crucial for determining the significance of a blockage.
4.3 MPI vs. Echocardiogram
Echocardiography uses ultrasound to assess heart structure and function. MPI focuses specifically on blood flow to the heart muscle.
5. Preparing for a Myocardial Perfusion Imaging Study
- Fasting: Patients are usually asked to fast for several hours before the test.
- Caffeine: Avoid caffeine-containing products.
- Medications: Discuss any medications with your doctor, as some may need to be adjusted.
6. The Heart Health Assessment Procedure: What to Expect
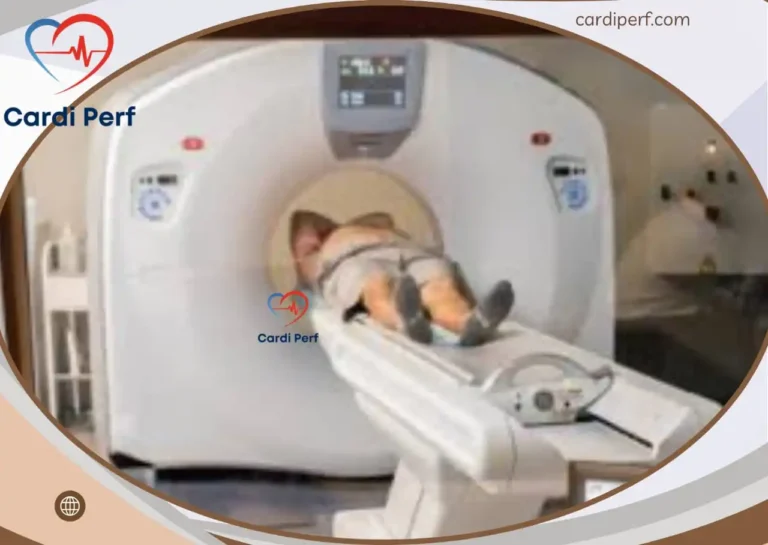
The procedure involves injecting the radioactive tracer, performing the stress test (exercise or pharmacological), and acquiring images with a special camera. The entire process may take a few hours.
7. Understanding Your Myocardial Perfusion Imaging Report
The report will describe the distribution of the tracer in the heart muscle. Areas of reduced uptake will be noted, indicating potential ischemia or infarction (heart attack).
8. Clinical Applications of Myocardial Perfusion Imaging
8.1 Diagnosing Coronary Artery Disease (CAD)
MPI is a cornerstone in diagnosing CAD, identifying areas of reduced blood flow caused by narrowed or blocked coronary arteries.
8.2 Assessing Heart Attack Risk
MPI helps assess the risk of future heart attacks by identifying areas of vulnerable myocardium.
8.3 Evaluating Chest Pain (Angina)
MPI is used to evaluate the cause of chest pain, differentiating between cardiac and non-cardiac causes.
8.4 Guiding Treatment Decisions
MPI results inform treatment decisions, helping cardiologists determine the best course of action for each patient.
9. Coronary Blood Flow in Special Populations
9.1 Patients with Pacemakers
MPI is generally safe for patients with pacemakers, but certain precautions may be necessary.
9.2 Patients with Diabetes
Diabetic patients are at increased risk for heart disease, and MPI plays a vital role in their evaluation.
10. Advancements in Heart Scan
Ongoing research is focused on improving MPI techniques, including reducing radiation exposure and enhancing image quality.
11. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- What are the benefits of myocardial perfusion Scan? (See Section 3)
- How is myocardial perfusion imaging different from a stress test? (See Section 4.1)
- Is myocardial perfusion imaging safe for patients with pacemakers? (See Section 9.1)
- How long does a myocardial perfusion imaging procedure take? (See Section 6)
- What are the side effects of myocardial perfusion imaging with stress test? (Discuss with your physician; generally safe, but some reactions to stress test medications are possible.)
- Where can I get a myocardial perfusion imaging scan in [city/region]? (Contact local hospitals and cardiology centers.)
- How much does myocardial perfusion imaging cost without insurance? (Contact your insurance provider and local facilities.)
- What is the accuracy of myocardial perfusion imaging for detecting CAD? (Highly accurate; discuss with your physician.)
- How to prepare for a myocardial perfusion imaging study? (See Section 5)
- Can myocardial perfusion imaging be used to diagnose heart failure? (While not the primary test for heart failure, it can provide supporting information.)
12. Conclusion: Empowering Cardiac Care with Myocardial Perfusion Imaging
Coronary Blood Flow Scan has revolutionized the diagnosis and management of heart disease. By providing valuable insights into myocardial blood flow, MPI empowers healthcare professionals to make informed decisions, ultimately improving patient outcomes and quality of life. If you have concerns about your cardiac health, discuss with your physician whether MPI is the right test for you. for update visit us at cardiperf.com