📌 Table of Contents
- Introduction to Computed Tomography Angiography CTA: What It Is & Why It Matters
- How CTA Works: The Science Behind the Scan
- Key Applications of CTA in Medical Diagnosis
- CTA vs. Other Imaging Modalities: Why It Stands Out
- Understanding CTA Results: What Radiologists Look For
- Risks & Contraindications: Who Should Avoid CTA?
- Innovations in CTA Technology: What’s Next?
- CTA for Patients and Families: What to Expect
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- Conclusion: The Future of CTA in Cardiovascular Care
🩺 Introduction to Computed Tomography Angiography CTA: What It Is & Why It Matters
Computed Tomography Angiography (CTA) is the gold standard for diagnosing vascular conditions. This advanced imaging technique provides high-resolution visualization of blood vessels, allowing for precise detection of blockages, aneurysms, and other cardiovascular conditions.. For patients and their families, CTA offers a fast and accurate way to detect life-threatening conditions without the need for invasive procedures.
💡 Key Takeaways:
- Uses contrast-enhanced CT scans for detailed vascular imaging.
- Essential in detecting conditions like aneurysms, stenosis, and pulmonary embolism.
- Faster and more precise than traditional angiography.
- Provides peace of mind with early and accurate diagnosis.
⚙️ How Computed Tomography Angiography CTA Works: The Science Behind the Scan
CTA utilizes advanced multislice CT technology along with an iodine-based contrast medium to highlight vascular structures. The scan captures multiple high-speed images, which are reconstructed into 3D models for detailed analysis.
For patients, this means:
- Minimal Discomfort: The procedure is quick and non-invasive.
- Rapid Results: Many scans are interpreted within 24 hours.
- Enhanced Precision: Allows doctors to see even small abnormalities.
🛠️ Process of Computed Tomography Angiography CTA Imaging:
- Patient Preparation: Fasting before the procedure and allergy screening for contrast dye.
- Contrast Injection: Intravenous contrast medium enhances vascular structures.
- High-Speed Imaging: Multislice CT scanner captures cross-sectional images.
- Image Reconstruction: 3D models are generated for accurate assessment.
🔬 Key Applications of Computed Tomography Angiography CTA in Medical Diagnosis
CTA is widely used in various medical fields, including cardiology, neurology, and oncology.
🩺 Cardiac & Vascular Applications
- Coronary CTA (CCTA) – Evaluates coronary artery disease (CAD), a major cause of heart attacks.
- Pulmonary CTA – Diagnoses pulmonary embolism (PE), a life-threatening lung condition.
- Aortic CTA – Detects aortic aneurysms and dissections, which can be fatal if untreated.
- Peripheral CTA – Assesses peripheral artery disease (PAD), which can lead to limb amputation if severe.
🧠 Neurological CTA
- Identifies carotid artery stenosis, a major risk factor for stroke.
- Detects cerebral aneurysms that may cause brain hemorrhage if they rupture.
🦵 Computed Tomography Angiography CTA for Peripheral Vascular Disease
- Maps arterial occlusions in the limbs.
- Aids in preoperative planning for vascular surgery.
🆚 CTA vs. Other Imaging Modalities: Why It Stands Out
CTA offers several advantages over traditional imaging techniques such as MRI, Doppler ultrasound, and conventional angiography.
📊 Comparative Analysis:
| Imaging Modality | Radiation Exposure | Speed | Invasiveness | Accuracy in Vascular Imaging |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CTA | Moderate | High | Non-Invasive | Excellent |
| MRI Angiography | None | Slow | Non-Invasive | Good |
| Doppler Ultrasound | None | Moderate | Non-Invasive | Limited |
| Conventional Angiography | High | Slow | Invasive | Gold Standard |
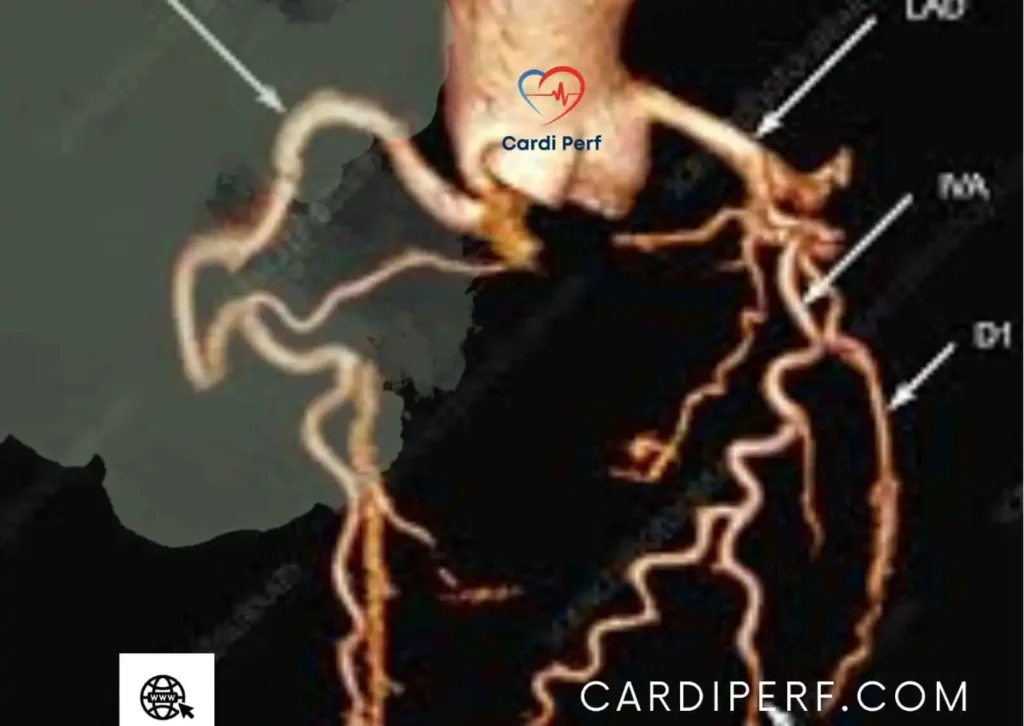
📖 Understanding Computed Tomography Angiography CTA Results: What Radiologists Look For
CTA reports focus on vascular patency, luminal narrowing, and anatomical anomalies.
🩻 Key Findings in a CTA Report
- Normal Findings: Open and smooth-flowing vessels.
- Atherosclerosis: Plaque buildup leading to stenosis.
- Aneurysms: Bulging weak points in arterial walls.
- Embolisms & Thrombosis: Clot formations causing obstruction.
⚠️ Risks & Contraindications: Who Should Avoid Computed Tomography Angiography CTA?
Although CTA is a powerful diagnostic tool, certain populations may face risks.
🚨 High-Risk Groups
- Kidney Disease Patients: Risk of contrast-induced nephropathy.
- Pregnant Women: Radiation exposure concerns.
- Iodine Allergy Patients: Potential for contrast reactions.
👨👩👧 Computed Tomography Angiography CTA for Patients and Families: What to Expect
For many patients, undergoing a CTA scan can be a source of anxiety. Understanding what to expect can ease concerns.
🏥 Before the Scan:
- Fasting may be required.
- Inform your doctor about any allergies or medical conditions.
- Wear loose, comfortable clothing.
📸 During the Scan:
- You will lie on a moving table inside the CT scanner.
- A contrast dye will be injected through an IV.
- The scan itself takes about 10-15 minutes.
📋 After the Scan:
- You can resume normal activities unless instructed otherwise.
- Drink plenty of fluids to flush out the contrast dye.
- Your doctor will review and discuss the results with you.
❓ Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is CTA used for?
CTA is primarily used to diagnose vascular conditions, including coronary artery disease, aneurysms, and pulmonary embolisms.
2. Is CTA painful?
No, CTA is a non-invasive procedure. Patients may feel a warm sensation when the contrast dye is injected.
3. How long does a CTA scan take?
The scan itself usually takes 10-15 minutes, but preparation and post-scan monitoring can extend the visit to about an hour.
4. Is CTA safe for children?
CTA is generally safe for children but is used only when necessary due to radiation exposure.
5. Can CTA detect heart attacks?
CTA can identify blockages that may lead to a heart attack but cannot detect an active heart attack.
For information and related article about cardiac Perfusion , cardiac surgery visit us at cardiperf.com