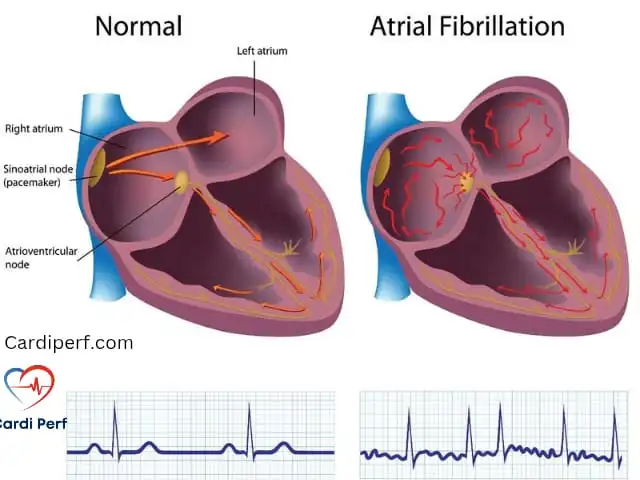
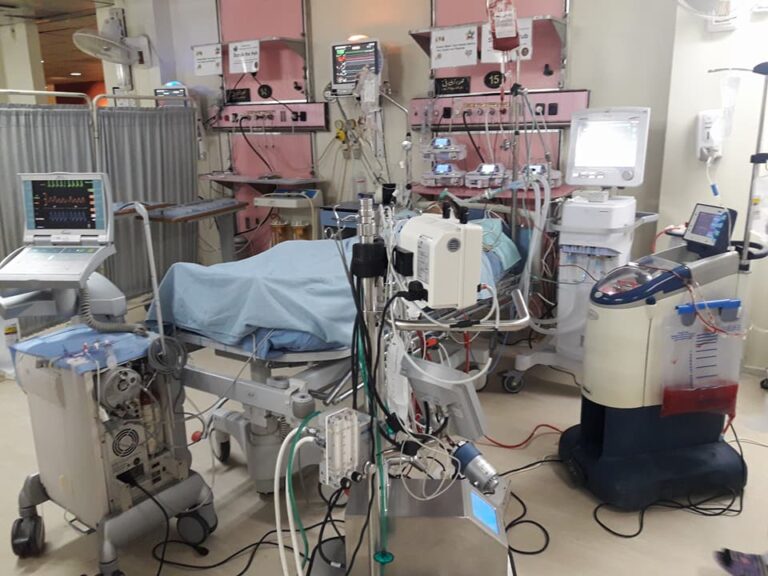
The Role of a Cardiovascular Perfusionist: Job Description, Salary, and Career Opportunities
Perfusionists play a critical role in cardiac surgeries and other medical procedures involving cardiopulmonary bypass. These highly skilled healthcare professionals operate complex machinery to ensure the patient’s heart and lungs are adequately supported during life-saving interventions. In addition to core responsibilities, perfusionists often specialize in areas such as ECMO, Impella devices, and isolated limb perfusion, broadening their scope of practice. This blog provides an in-depth look at the perfusionist’s job description, salary prospects, and career opportunities, focusing on specialized roles and strategies for job placement.
What Does a Perfusionist Do?
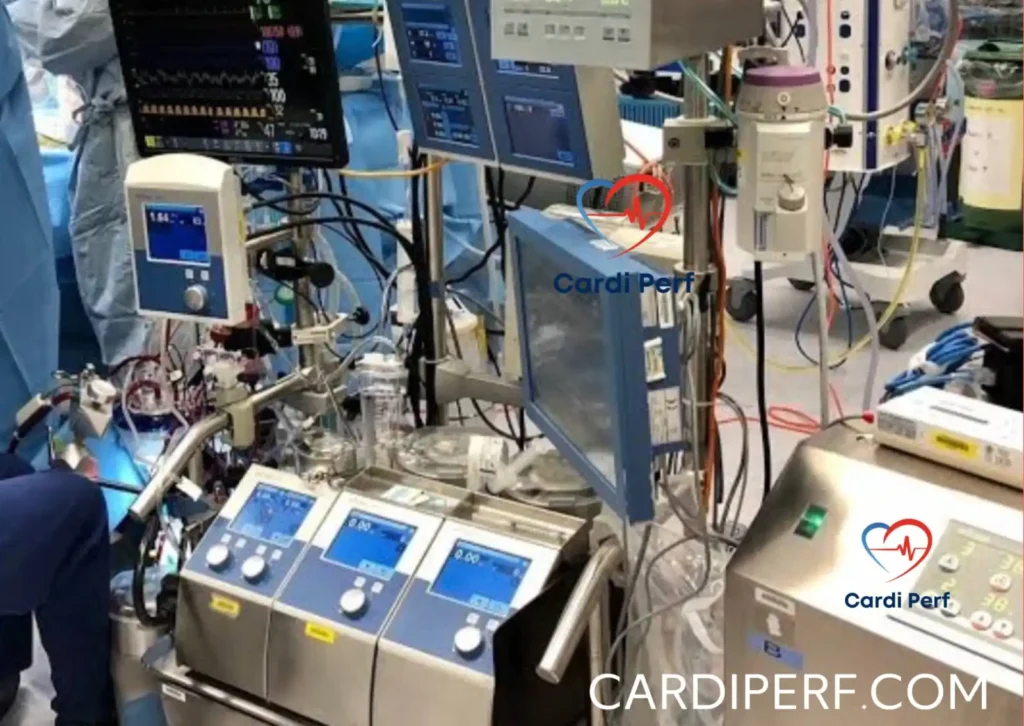
Primary Responsibilities
A cardiovascular perfusionist operates the heart-lung machine, also known as the cardiopulmonary bypass machine, during surgeries such as open-heart procedures. Their responsibilities include:
- Pre-Surgery Preparation:
- Reviewing patient medical histories to tailor perfusion strategies.
- Ensuring all equipment, including oxygenators and cannulas, is functioning properly.
- Intraoperative Support:
- Managing blood flow and oxygen levels using the heart-lung machine.
- Monitoring critical parameters such as blood pressure, temperature, and ACT levels.
- Administering medications, blood products, or anticoagulants as needed.
- Postoperative Duties:
- Assisting with the weaning process from bypass support.
- Cleaning, maintaining, and troubleshooting perfusion equipment.
Specialized Roles
Perfusionists often expand their expertise into specialized areas, such as:
Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation (ECMO) Specialist:
Managing ECMO systems for patients with severe cardiac or respiratory failure.
Collaborating with intensivists to optimize outcomes during long-term ECMO support.
Operating left ventricular assist devices (LVADs) like Impella to provide temporary cardiac support.
Monitoring hemodynamic parameters and ensuring device functionality.
Cell Saver Technician:
Operating autotransfusion devices to recover and process a patient’s blood during surgery.
Reducing the need for donor blood and minimizing transfusion risks.
Isolated Limb Perfusion Specialist:
Delivering targeted chemotherapy to limbs affected by cancer, sparing systemic toxicity.
Collaborating with oncologists to execute precise perfusion protocols.
Required Skills and Education
Educational Pathway
- Undergraduate Degree: A bachelor’s degree in a science-related field (e.g., biology, chemistry, or health sciences) is often required.
- Perfusionist Training Program: Completing an accredited cardiovascular perfusion program, typically lasting 2 years.
- Certification: Passing the certification exam administered by the American Board of Cardiovascular Perfusion (ABCP) or equivalent.
Key Skills
- Proficiency in advanced medical technologies.
- Strong critical thinking and problem-solving abilities.
- Ability to work under pressure in high-stakes environments.
- Excellent communication and teamwork skills.
Perfusionist Salary Overview
Average Salary by Region
- United States: \$110,000–\$150,000 annually, with experienced professionals earning upwards of \$180,000.
- Europe: €60,000–€90,000 depending on the country and experience level.
- Middle East: High demand in countries like the UAE and Saudi Arabia, offering tax-free salaries ranging from \$90,000 to \$130,000.
Factors Influencing Salary
- Experience: Senior perfusionists often command higher salaries due to their expertise.
- Location: Salaries vary widely based on geographical demand and cost of living.
- Specialization: Expertise in ECMO, Impella devices, or pediatric perfusion can significantly increase earning potential.
Job Placement for Perfusionists
Strategies for Finding a Job
- Networking: Join professional organizations such as the American Society of Extra-Corporeal Technology (AmSECT) to connect with industry peers.
- Job Boards: Utilize specialized platforms like PerfusionCommunity.com or healthcare-specific job portals.
- Internships and Clinical Rotations: Leverage training programs to secure mentorship and hands-on experience.
- LinkedIn Optimization: Maintain an updated profile highlighting certifications, clinical experience, and technical skills.
High-Demand Sectors
- Cardiac Surgery Centers: Hospitals with high volumes of cardiac procedures often seek skilled perfusionists.
- ECMO Programs: The rising use of ECMO in critical care has created specialized roles for perfusionists.
- Pediatric Hospitals: Specialized training in neonatal and pediatric perfusion is highly valued.
- Isolated Limb Perfusion Clinics: Expanding opportunities in oncology-focused facilities.
- Research and Development: Opportunities exist with medical device companies developing perfusion technologies.
Challenges and Rewards in the Perfusionist Profession
Challenges
- High Stress Levels: The role demands constant focus and precision in life-threatening scenarios.
- On-Call Responsibilities: Perfusionists often work long hours and may be on call for emergencies.
- Continuous Learning: Staying updated with technological advancements and certifications is essential.
Rewards
- Life-Saving Impact: Few careers offer the satisfaction of directly contributing to saving lives.
- Professional Recognition: Perfusionists are highly respected members of the surgical team.
- Career Growth: Opportunities for specialization and leadership roles abound in this field.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
For Aspiring Perfusionists
- How long does it take to become a perfusionist?\
It typically takes 6–8 years, including a bachelor’s degree and specialized training. - Is the job market competitive?\
Demand for perfusionists is high globally, especially in regions with growing cardiac care facilities. - What is the most rewarding aspect of being a perfusionist?\
Making a tangible difference in patient outcomes during critical procedures.
For Employers and Institutions
- What qualities should I look for when hiring a perfusionist?\
Seek candidates with strong technical skills, critical thinking, and the ability to thrive under pressure. - How can I retain skilled perfusionists?\
Offer competitive salaries, opportunities for continuing education, and a supportive work environment.
Conclusion
The role of a cardiovascular perfusionist is indispensable in modern healthcare, offering both challenges and immense rewards. With competitive salaries and opportunities for specialization, it remains an attractive career choice for those passionate about critical care and advanced medical technology. Whether you’re an aspiring perfusionist or a healthcare institution looking to build a robust surgical team, understanding the nuances of this profession is crucial.
Stay informed about the latest trends and opportunities in perfusion science by visiting cardiperf.com, your trusted source for expert insights.