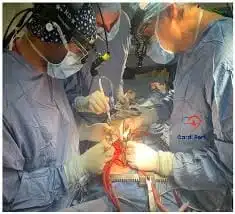
Cardiovascular perfusion is an important part of heart surgeries because perfusionists work to keep blood circulating while the heart is stopped. This crucial specialty field makes sure organs are continually supplied with oxygen and nutrients, helping to keep patients healthy during these delicate procedures.
Cardiovascular perfusionists run heart-lung machines, which assume the heart’s function temporarily during surgeries. These highly trained specialists are an indispensable part of most every open heart surgery, including life-saving coronary artery bypass grafts and valve replacements. Their work protects the surgical team—ensuring the patient’s physiological stability is never in question.
Learning about this field’s impact on humanity’s future underscores how crucial precision and care will be to the new healthcare landscape. It is through cardiovascular perfusion that patients are provided the vital support they need, highlighting the passion and skill it takes to deliver positive surgical results.
As with all essential practices, this important field continues to grow, helping more patients survive and recover from heart surgery.
Key Takeaways
- Cardiovascular perfusion is vital in delivering oxygenated blood to all body tissues, maintaining not only cardiac health, but systemic body homeostasis. It helps ensure that organs are properly nourished and oxygenated so they can perform at their peak levels.
- Perfusionists have a crucial role during an operation. They control blood flow to deliver sufficient oxygen and nutrients to tissues, while promoting the rapid clearance of metabolic by-products.
- Cardiac perfusion is all about maintaining adequate blood flow to the heart muscle. Medical professionals observe this process very carefully during procedures to make sure everything is working perfectly.
- The key to effective blood flow is hemodynamics. Vessel diameter and elasticity are important factors to consider when discussing blood perfusion and cardiovascular health overall.
- Healthy lifestyle habits, including regular exercise, improve a perfusion, whereas smoking and obesity are detrimental to perfusion. Environmental justice is an issue when it comes to perfusion health.
- Medications that can impair blood flow and perfusion. This is why medication management is so important for patients with cardiovascular conditions, to be able to live their best lives.
What is Cardiovascular Perfusion
Cardiovascular perfusion refers to the act of oxygenated blood through the circulatory system to the body’s tissues. It is essential to both keeping our hearts healthy and carrying out our day-to-day bodily functions. Proper perfusion is vital in supporting the demands of the body’s complex organs, providing them the nutrients and oxygen needed to operate smoothly and efficiently.
During complicated heart surgeries cardiovascular perfusionists are the unsung heroes, regulating blood flow and oxygen delivery.
Definition of Perfusion
Cardiovascular perfusion science is essential as it involves the process of delivering blood or lymphatic fluid to organs or tissues. This critical perfusion technology ensures that cells receive vital nutrients and oxygen, enabling metabolism and waste removal, which is fundamental for healing and normal body function.
Role in Heart Health
As a result, maintaining adequate perfusion is critical in the prevention of heart disease. When blood flow becomes compromised, it can result in dangerous conditions such as a myocardial infarction. Cardiovascular perfusionists make sure hearts keep beating during surgeries by running the cardiopulmonary bypass machine.
They create an important link in the surgical chain, collaborating with cardiothoracic surgeons, anesthesiologists and surgical nurses. Perfusionists oversee a variety of tasks, from operating CPB machinery to controlling blood circulation during operations. Their expertise demands no less than four years of education, comprising a bachelor’s degree and the successful completion of an accredited perfusion program.
Today, more than 3,700 perfusionists—keeping pace with a growing demand—are on the front lines in the U.S. They monitor blood chemistry and often employ intra-aortic balloon pump to maximize perfusion. These professionals are truly the unsung heroes when it comes to ensuring successful surgical outcomes, and optimal patient safety and welfare.
Understanding Cardiac Perfusion
1. Definition and Importance
Cardiac perfusion refers to the delivery of blood specifically to the heart muscle, ensuring it receives the oxygen and nutrients needed to function. This process is vital for maintaining the heart’s metabolic needs, supporting its continuous activity. Effective cardiac perfusion is crucial for overall cardiovascular health and aids in patient recovery by preventing heart tissue damage.
Techniques like Cardiac Magnetic Resonance Perfusion (CMRP) imaging, known for its non-ionizing and versatile capabilities, enhance our understanding by providing functional and anatomical insights. These imaging methods are pivotal, similar to how perfusion is used to evaluate tumors.
2. Key Physiological Processes
The heart’s pumping action is essential in cardiac perfusion, as it actively pumps blood through coronary arteries. This continuous flow is controlled by dynamic vascular resistance and compliance processes, affecting volumetric perfusion rates.
As an illustration, during medical procedures such as coronary angiography, pharmacologic vasodilatation with agents such as adenosine are employed to accentuate regional flow disparities. Innovations in imaging, including CT and MR, are now able to interpret these changes, providing a much more comprehensive picture of perfusion dynamics.
The use of contrast agents, specifically their uptake in myocardial tissue, changing signal intensity, helps to further allow for detailed evaluation.
3. Differences from Cardiovascular Perfusion
Whereas cardiac perfusion concerns itself exclusively with the heart, cardiovascular perfusion encompasses the body’s entire circulatory system. This distinction is important in clinical practice, as it drives how patients are cared for.
The TransMedics Organ Care System represents the pinnacle of cardiac-specific perfusion, a device to keep donor hearts alive and healthy. Whether on a day, evening, or weekend shift, cardiovascular perfusionists push the envelope of support throughout the entire circulatory system.
Their function, created, and first used by technicians in the early days of open-heart surgery, is still crucial and highly relevant in today’s healthcare.
Physiological Processes in Perfusion

Blood Flow Mechanisms
Blood flow within the cardiovascular system is governed by the laws of hemodynamics, propelling blood vigorously throughout the body. Arteries and veins have different physiological roles in this process. High-pressure dynamics of arterial blood flow drive oxygenated blood from the heart to all tissues.
Conversely, venous flow is unique in that it returns deoxygenated blood back to the heart under lower pressure. Vessel elasticity and diameter hugely impact flow rate. For example, wider, more elastic vessels increase laminar flow, leading to faster flow and better perfusion.
Vessels with excessive constriction or blockage can restrict flow, making perfusion more or less effective.
Oxygen and Nutrient Delivery
Perfusion is essential for the delivery of oxygen and nutrients to tissues. Hemoglobin in red blood cells binds oxygen, making transport easier. This physiological process is critical for effective perfusion.
During cardiac surgery, perfusionists ensure and monitor optimal oxygen delivery to tissues, maintaining tissue oxygenation and adequacy. Almost every cell is located within 0.004 to 0.008 inches of a capillary, maximizing the exchange of nutrients and wastes.
Perfusion systems better replicate organ physiology by constantly providing a fresh supply of nutrients while flushing out waste products, which more closely mimics metabolic function.
Waste Removal Processes
Removal of wastes efficiently is equally as critical for cellular homeostasis. The circulatory system moves metabolic waste products, including carbon dioxide, away from tissues. Organs such as the kidneys and liver are vital in the processing and excretion of these wastes.
Without this efficient clearance, cellular function may diminish. The removal process is so efficient that gas diffusion equilibrates almost instantly, preventing hypoxic or hypercapnic cellular states.
Factors Affecting Perfusion
Common Medical Conditions
Medical pathologies such as atherosclerosis and heart failure frequently limit perfusion. Atherosclerosis is the hardening of arteries due to the build-up of fatty deposits which can thicken arteries and restrict blood flow. This can compromise oxygen delivery to vital organs, causing fatigue and possibly organ injury.
Heart failure is a complex condition that happens when the heart is no longer able to pump blood effectively. This causes increased fluid retention and a lowered delivery of oxygen to the tissues. Diabetes and hypertension play a huge role in limiting perfusion. If diabetes is akin to rusting the blood vessels, hypertension is like pressurizing them.
The effects are serious, often damaging the heart, brain, and kidneys, leading to a cascading and severe decline in overall health.
Lifestyle and Environmental Factors
Lifestyle factors play a significant role in perfusion health. Smoking, obesity, and sedentary behavior have been identified as some of the worst offenders. Tobacco use harms blood vessels and obesity puts excess strain on the heart, forcing it to work harder to pump blood.
A lifestyle that’s mostly inactive makes circulation slower and less effective, resulting in poor blood flow. Conversely, daily exercise increases circulation, increasing blood volume and flow and thus perfusion to the area.
Similar effects come from environmental factors, such as pollution and extreme temperatures. In high altitudes, there is a lower availability of oxygen, which can further inhibit the body’s ability to perfuse all organs adequately.
At the same time, when temperatures are extreme, blood vessels are forced to constrict or dilate, limiting blood flow.
Impact of Medications
Medications can be of great importance to perfusion as well. Drugs such as anticoagulants and vasodilators may enhance perfusion by inhibiting clot formation and dilating blood vessels, respectively. These are often used to treat underlying conditions that impact perfusion.
Some medications may produce side effects that worsen perfusion. Thus, effective medication management by health care providers for patients at risk for cardiovascular disease can help achieve perfusion and improve health outcomes.
Conclusion
Cardiovascular perfusion is at the heart of understanding cardiovascular health. It teaches us about the basic flow of blood in the body and the factors that can influence this flow. Through understanding the complex processes and multifactorial influences on perfusion, we can understand the critical role it plays in maintaining health. In addition, this knowledge gives us the ability to take control of our health and make intentional decisions regarding lifestyle and medical care.
As you explore this exciting new field, don’t forget that the state of your heart’s health can have a profound effect on your life. Keep reading and traveling safe. Do make cardiovascular health a priority by getting active, eating healthy and scheduling regular health visits. Let’s protect the heart of our nation and make sure the blood keeps flowing. Participate in policy discussions, get technical assistance from experts, and help build a healthier future.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is cardiovascular perfusion?
Cardiovascular perfusion science is essential for ensuring blood circulates through the heart and vascular system, allowing oxygen and nutrients to reach all body tissues. This process is vital for the health and function of every organ and cell in the body.
Why is cardiac perfusion important?
Cardiac perfusion is critical in the field of cardiovascular perfusion science for providing myocardial tissues with oxygen and nutrients, which supports optimal heart function and health while avoiding ischemic heart damage.
What physiological processes are involved in perfusion?
Perfusion is the process of blood circulation, oxygen exchange, and nutrient delivery to tissues, crucial in cardiovascular perfusion science. This encompasses cardiac output, vasodilation, and microcirculation, vital for aspiring cardiovascular perfusionists.
What factors affect perfusion?
Perfusion is influenced by various factors, including blood pressure, heart rate, and vascular health. Additionally, fluid status and oxygenation status play crucial roles, while the presence of occlusion or disease can significantly impact clinical perfusion. Healthy habits will do the most to help aspiring cardiovascular perfusionists maintain optimal perfusion at any age.
How can I improve my cardiovascular perfusion?
Support cardiovascular perfusion science through exercise, a healthy diet, and stress management techniques. Staying active with regular exercise increases circulation, while a diet rich in fruits and vegetables helps prevent damage to blood vessels, enhancing overall cardiovascular function.
What are the consequences of poor perfusion?
Chronic under-perfusion can lead to serious events such as heart attacks or strokes, resulting in tissue necrosis and organ dysfunction. With early detection and management, aspiring cardiovascular perfusionists in healthcare settings can help patients thrive despite this condition.
Can lifestyle changes enhance perfusion?
Lifestyle changes can dramatically affect perfusion, as regular exercise and a heart-healthy diet improve blood flow, thereby enhancing cardiovascular health and reducing dangerous complications related to the perfusion profession.